
Jul 12 2025 | २०८२, असार २८ गते
Jul 12 2025 | २०८२, असार २८ गते

The torrential rains have caused massive floods across various parts of Nepal whilst damaging various critical infrastructures.
But,beyond that there's a higher risk of outbreak of other infectious diseases in the flood-affected areas including the transmission of several water-borne ,air-borne,food-borne as well as vector-borne diseases respectively.
The World Health Organisation (WHO) has enlisted the following diseases in particular that are worth looking out for during and post floods.
Vector-borne diseases like Dengue,Malaria:
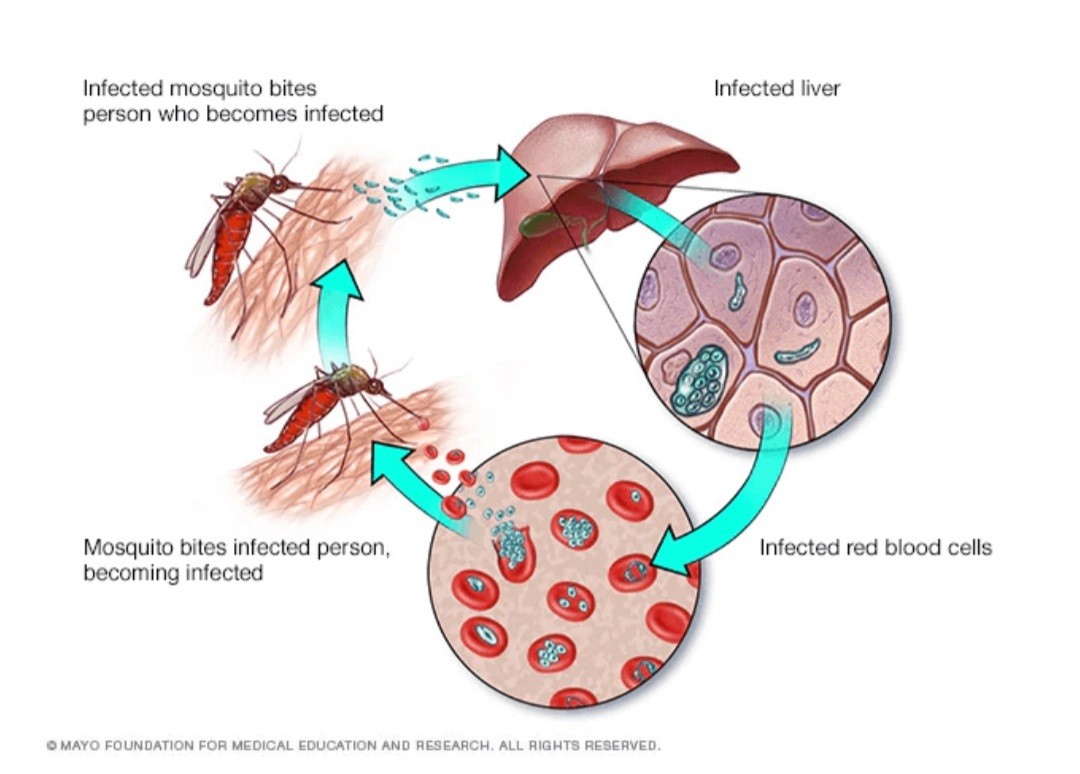
In this type,mosquitoes serve as pathogens to transmit either malaria or dengue epidemic as the floodwater act as a prime breeding sites for the proliferation of mosquitoes.
Water-borne diseases like Cholera,Typhoid fever,Leptospirosis,Hepatitis A,Jaundice:
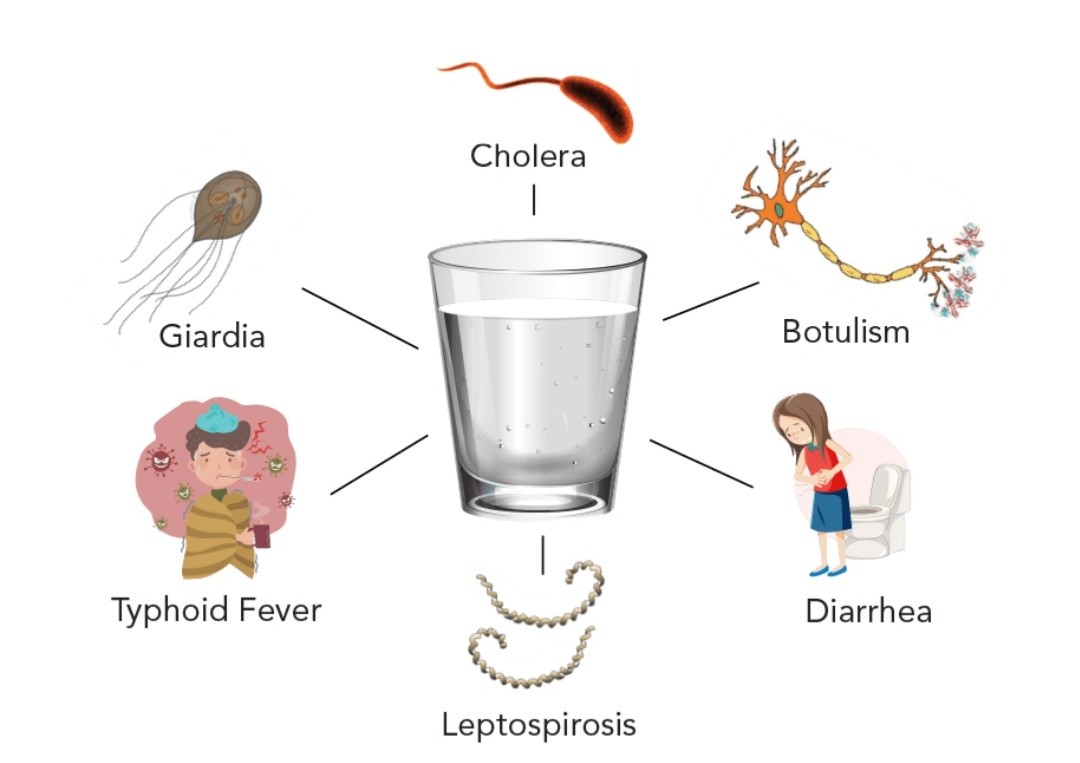
image courtesy: Mfine
Due to lack of access of clean water or through faecal contaminated water,the diarrhoeal epidemics,among others occur as the flood water mixes up with the sewage water and thus becomes polluted.
As we know that, many displaced people are sheltering into overcrowded camps with limited access to food,safe drinking water facilities or any proper sanitation measures.
This infact can give a rise to another ongoing problem of "Coronavirus surge" because our country is still baffling with COVID-19 plus with the spread of this deadly virus might pose a threat against keeping people safe in the shelter homes.
Thus,it calls for an immediate establishment of a "Disaster Evacuation shelter" in the light of the pandemic alongside maintaining the health protocols within the confined space.
WHO has prepared the following guidelines to check on the public health aspects of the natural disaster in the midst of COVID-19.
https://iris.wpro.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665.1/14603/WPR-DSE-2020-033-eng.pdf
The major highlights from the released report states that,
In the context of Nepal,however one can only assume if the above strategies would be applied or not since the country has its limitations owing to financial constraints; inadequacy in stipulating emergency outreach response and lack of skill human resources.
The following table shows the breakdown of the infectious disease transference.
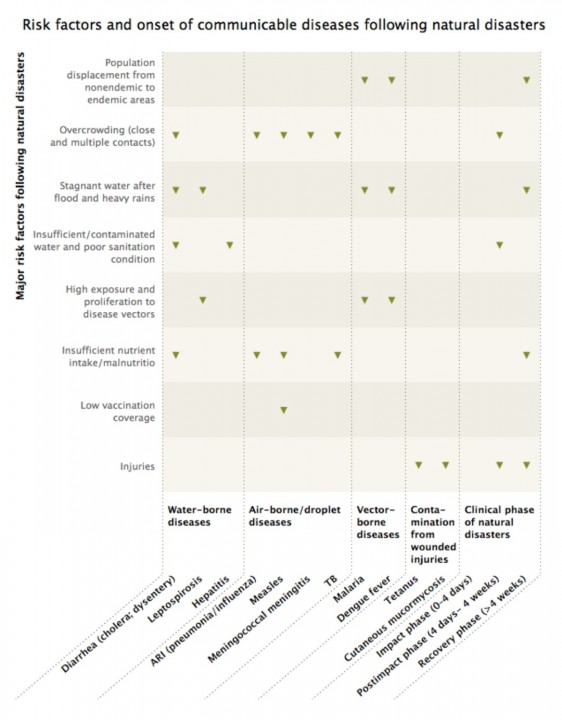
source: UN University
Preventive measures
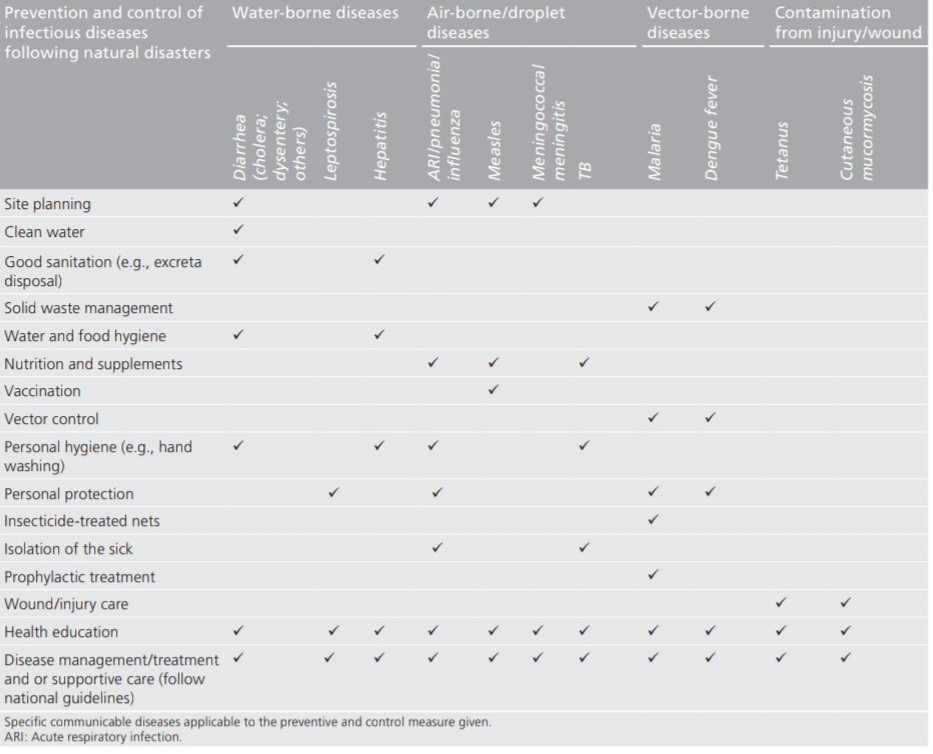
source : UN University.
But,in a larger context the government should strengthen the national surveillance system, distribute the emergency relief materials efficiently ,provide adequate safe drinking water, regulate the nutritious food supplies, monitor proper sanitation facility and recruiting health personnel to meet with the health needs of the vulnerable group.

Meanwhile,The Ministry of Health and Population has already formed Rapid Response Group at all local levels under the Division of Epidemiology and Disease Control to mitigate the possible harms of the communicable disease.
© 2025 All right reserved to onlinepatrika.com | Site By : Sobij
© 2025 All right reserved to onlinepatrika.com | Site By : Sobij